Proteins and Amino Acids
2017-10-02
What kinds of materials go into building a factory?

wikipedia




 See International
See International
How does one chemical (protein) achieve such a vast array of functions?






Conceptual goals
- The sequence of a protein determines is structure, which determines its function
- Understand how concatenating relatively few amino acids can lead to a huge diversity of possible functional proteins.
Skill goals
- Identify the amino acids based on their chemical structure.
- Reason about how their individual chemistry leads to distinct biological roles.
The power of combinatorics!
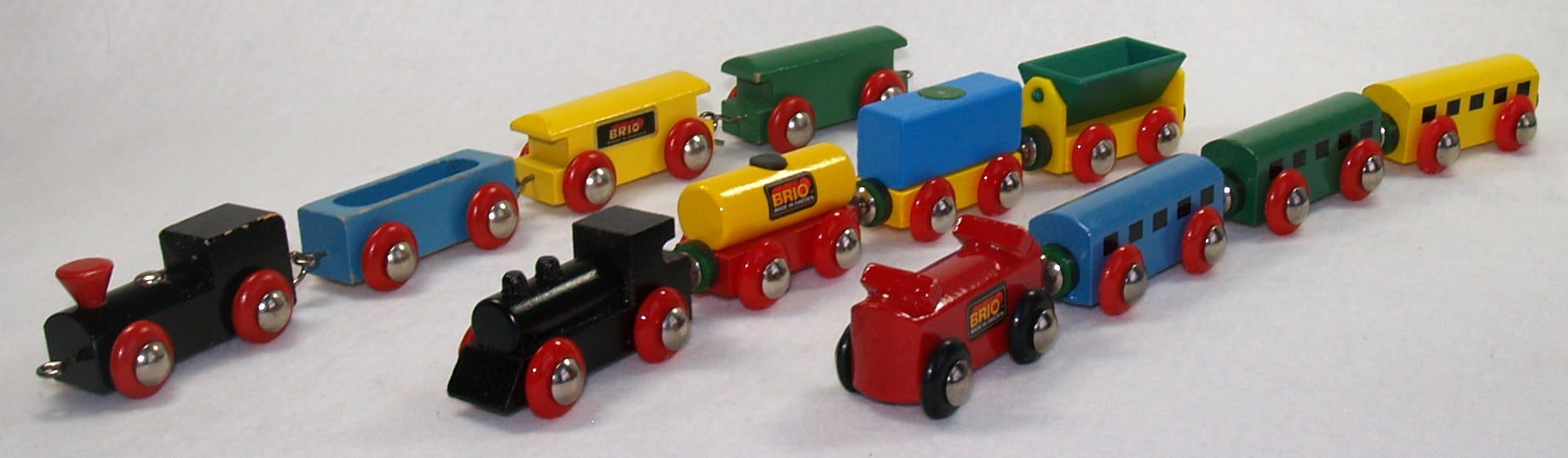

- Directional (has front and back)
- You can make it as long as you want
- You can swap in any car at any point in the train
On your handout, circle amino acids whose sidechain participates in:
- hydrophobic effect
- Van der Waal's
- hydrogen bonds
- ionic interactions
- covalent bonds (without enzymatic help)
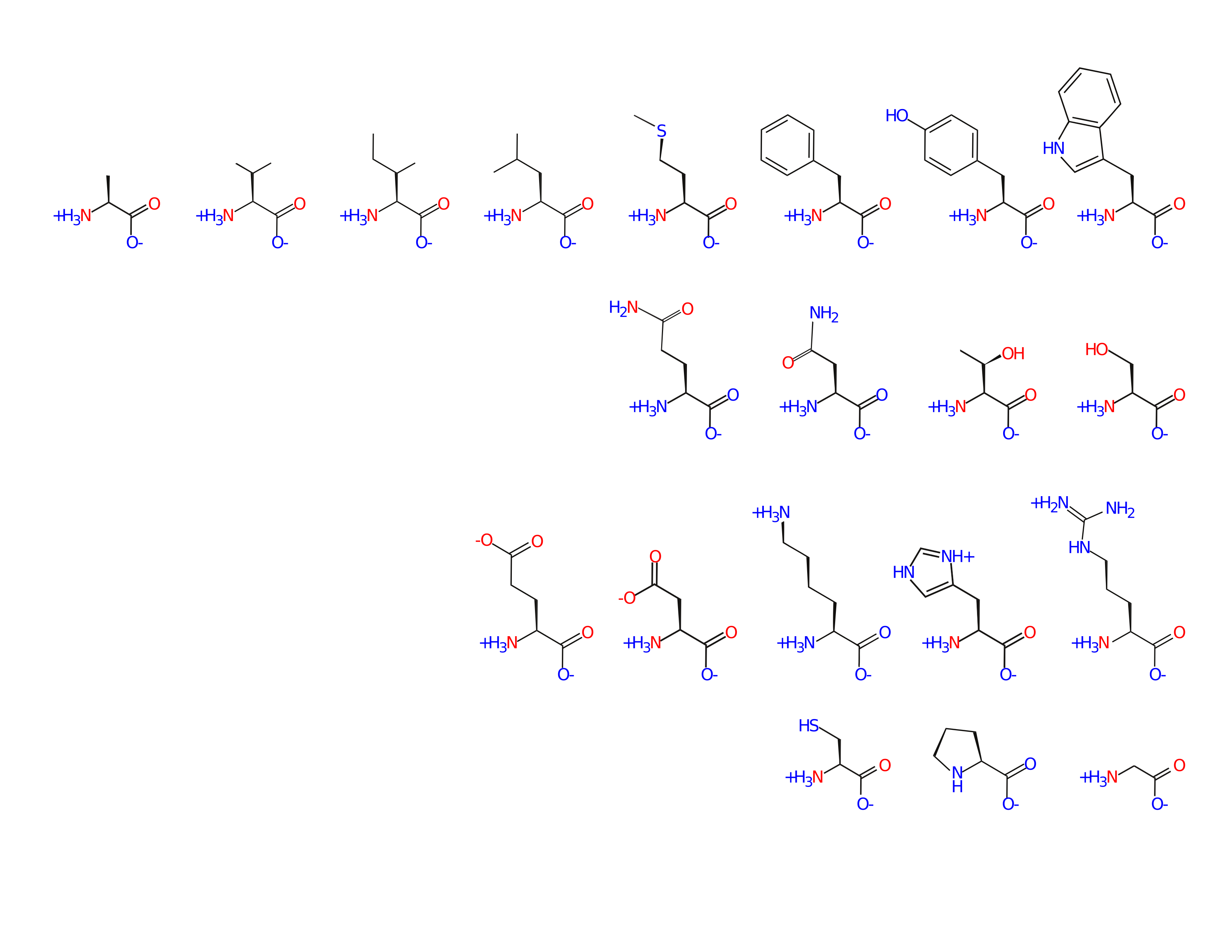

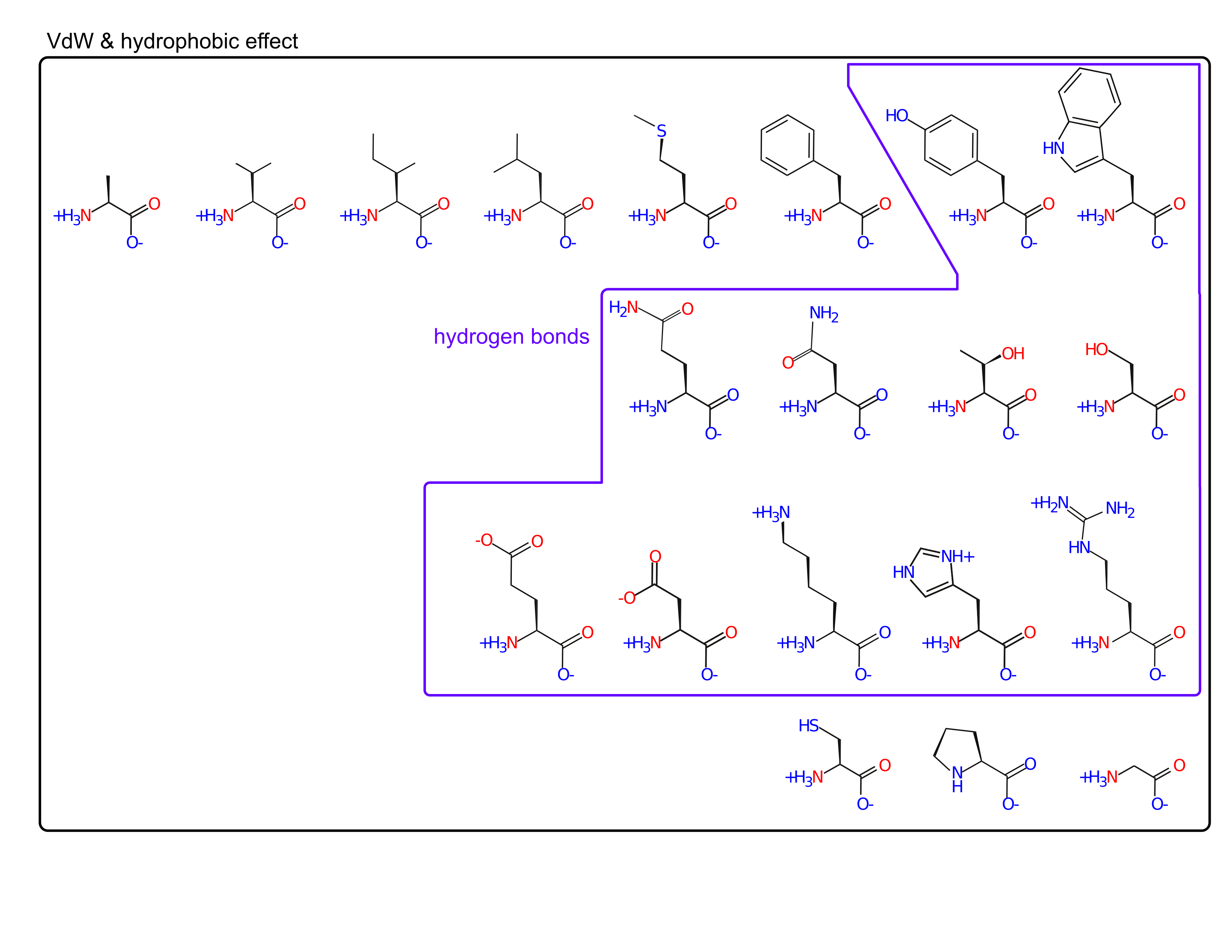
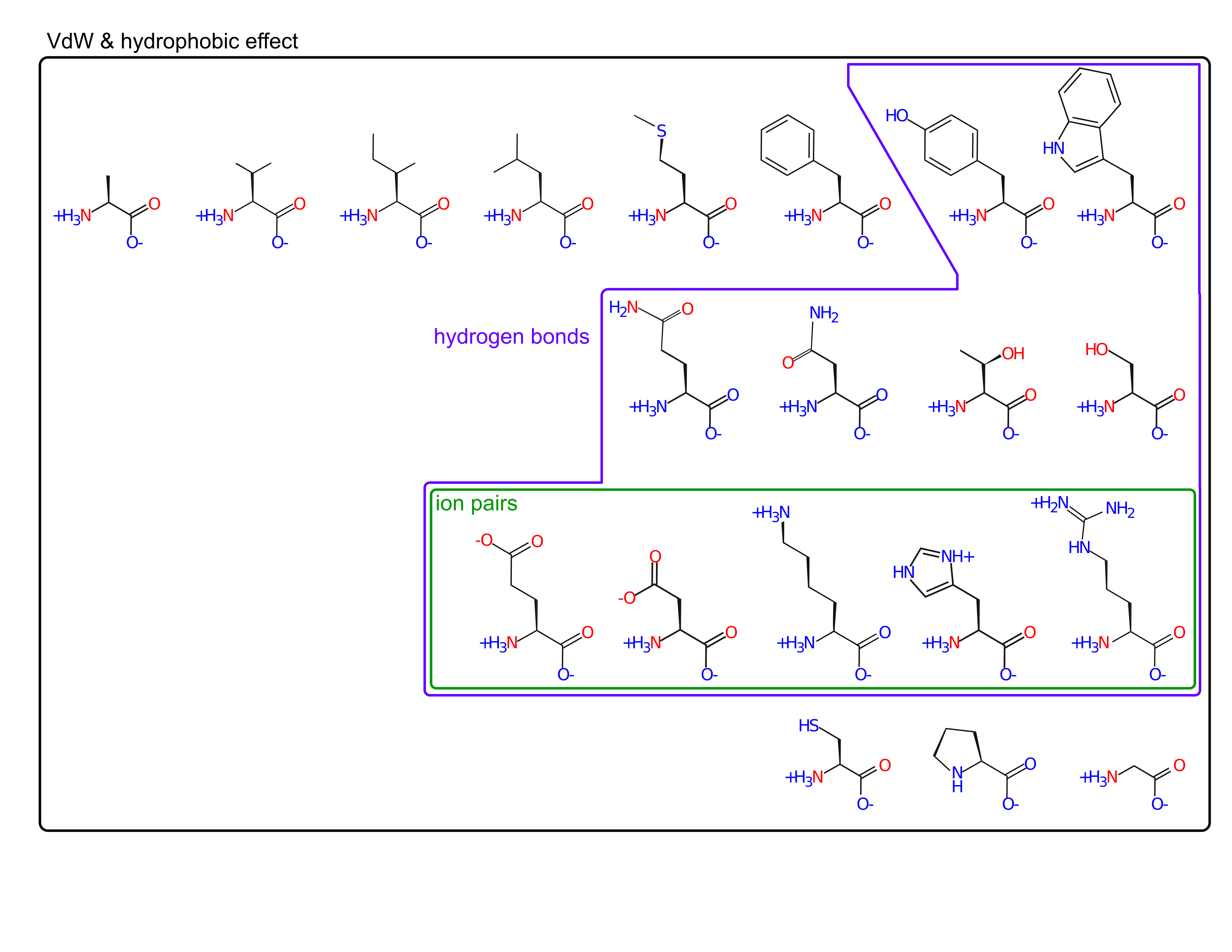
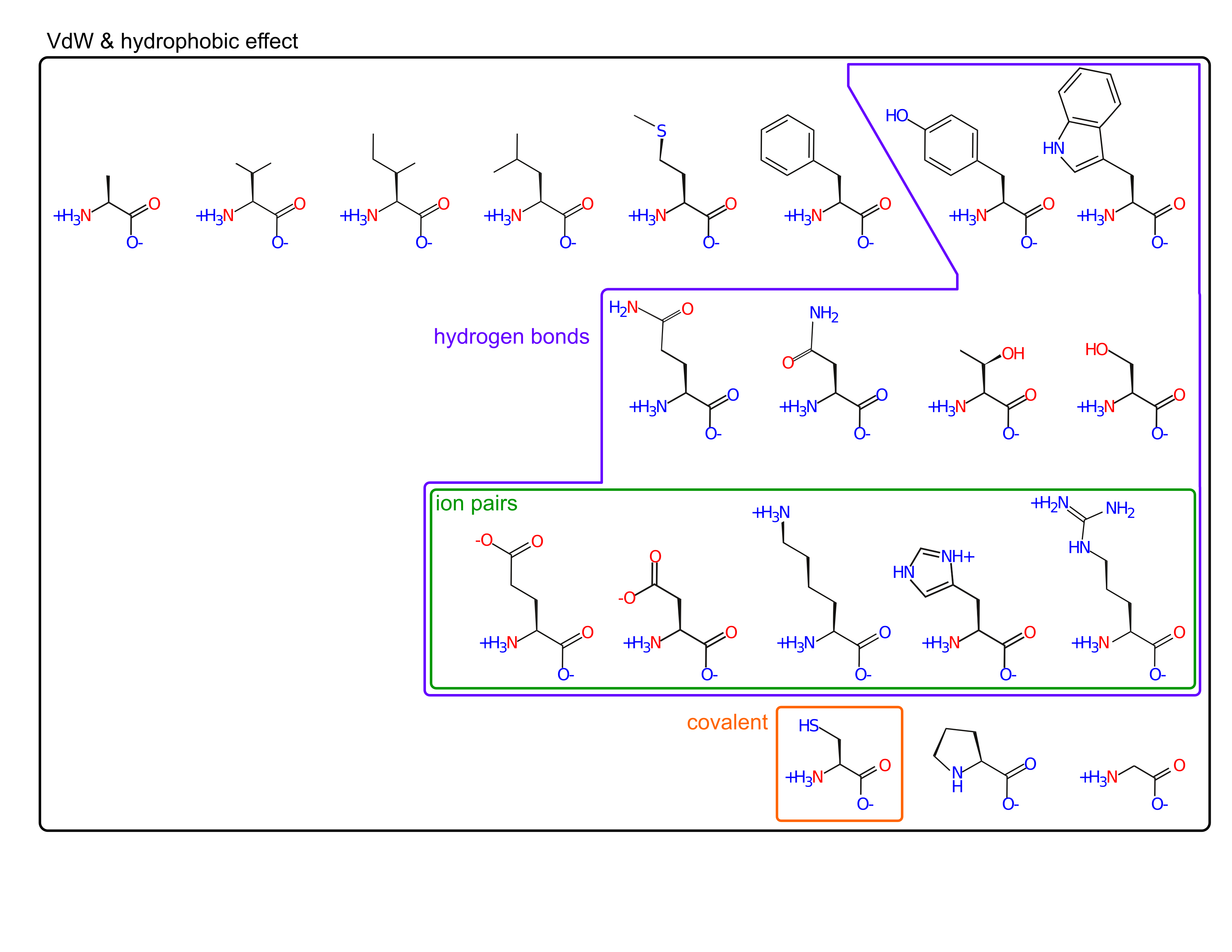

Amino acids fill a large volume of "property space"
Key points:
- Proteins are formed from amino acids, arranged into a chain
- Chain is formed by a series of peptide bonds
- Because there are 20 naturally-occuring amino acids, a vast number of sequences are possible
- These 20 amino acids cover a wide range of chemical properties