Midterm #2: 7-9 pm on Wednesday, November 8, McKenzie 240C
Review Session: 7-9 pm on Thursday, November 2 (tomorrow), Lawrence 115
Membrane proteins
2017-11-01
Conceptual goals
- Understand how membrane proteins can act as gatekeepers to move material in and out of the cell
- Understand the basic molecular mechanisms by which it achieves this function
Skill goals
- Predict whether a protein will be able transport a molecule based on the structure of the membrane protein and the molecule
- Reason about passive versus active transport
Membrane design features
- Spontaneous assembly
- Flexible
- Divisible
- Selectively permeable
- Can "host" other molecules
Phospholipid has 4 basic parts: lipid tails, glycerol, phosphate, head group
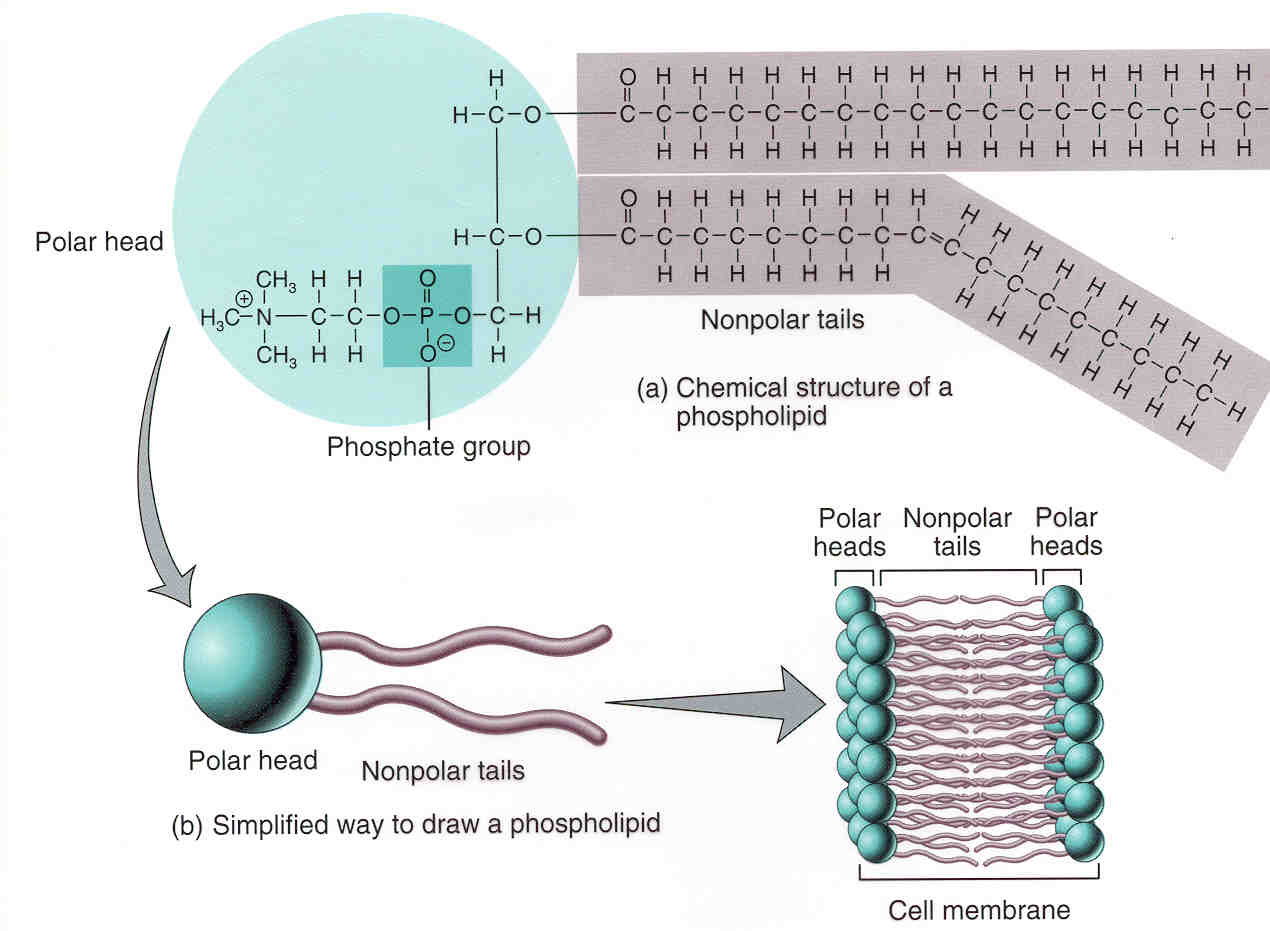
Credit: smc.edu
Phospholipids form bilayers
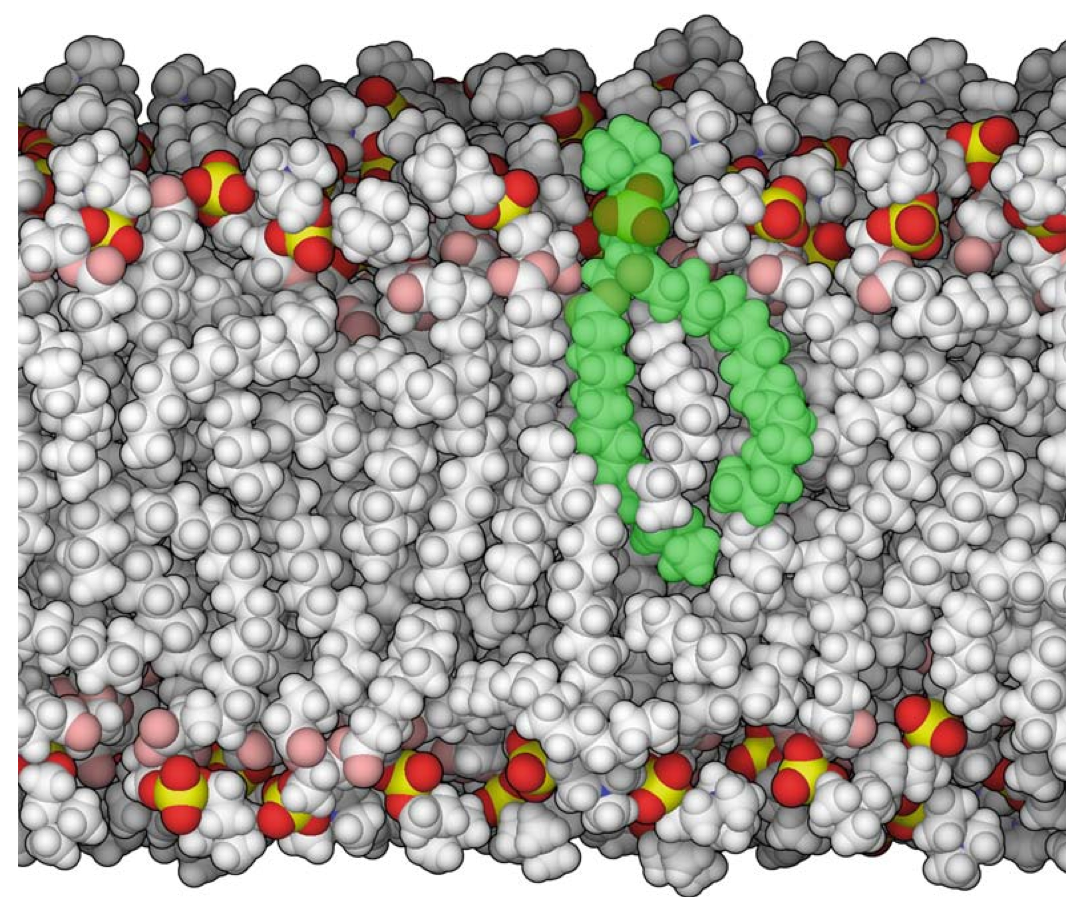
Credit: Goodsell
Selective permeability: Only some molecules can pass through the bilayer
Which molecules would be able to pass through a bilayer?
- $Na^{+}$ No.
- steroid (estrogen, testosterone) Yes.
- A protein molecule No.
- $H_{2}O$ Yes.
Only small, uncharged molecules can diffuse across a membrane
Membranes host proteins and sugars for diverse functions in transport, signaling, and molecular recognition
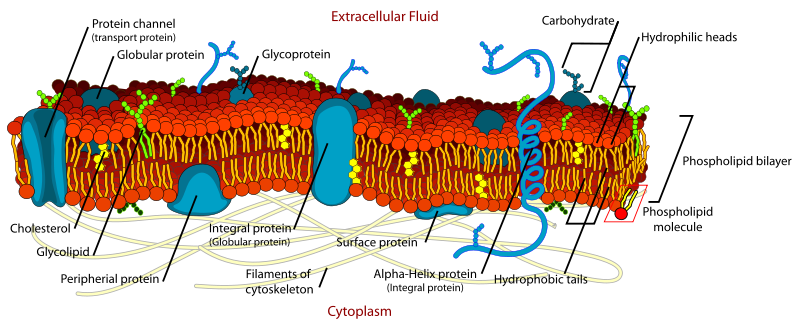 Credit: https://teaching.ncl.ac.uk/
Credit: https://teaching.ncl.ac.uk/
Focus today on integral membrane proteins that move material across it
- Why are transport membrane proteins needed?
- Transport selectivity
- Passive versus active transport
- Nerve signal transmission
Why are transport proteins needed?
Permeability: some stuff can't pass the bilayer
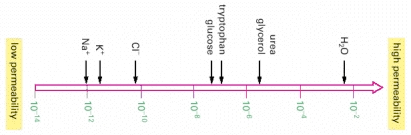
Why are transport proteins needed?
Moving a potassium ion ($K^{+}$) across a bilayer is hard because:
- It can't fit through the bilayer
- Removing hydrogen bonds from charged atom is unfavorable
- It gets stuck interacting with the lipid tails
Answer: 2
Why are transport proteins needed?
Control. If transport proteins only open and close in certain circumstances, this leads to regulated behavior.
- Why are transport membrane proteins needed? (permeability and control)
- Transport selectivity
- Passive versus active transport
- Nerve signal transmission
Selectivity: the case of aquaporin
Water can get across a bilayer, but it's slow
There are cases where this needs to go faster and be controlled. Where might this be?
Kidneys, "epithelial" cells exposed to environment...
How would you build something that would letter water through but not these other molecules?
- sodium ion ($Na+$)
- glucose ($C_{6}H_{12}O_{6}$)
- chloride ion ($Cl^{-}$)
Answer: make it so only water can fit and be satisfied.
Water goes single-file and has to pass by positively charged residues in the channel.
How does aquaporin filter the following molecules?
- water ($H_{2}O$) lets through
- sodium ion ($Na+$) positive charge
- glucose ($C_{6}H_{12}O_{6}$) size
- chloride ion ($Cl^{-}$) size
Chloride ion is much larger than water
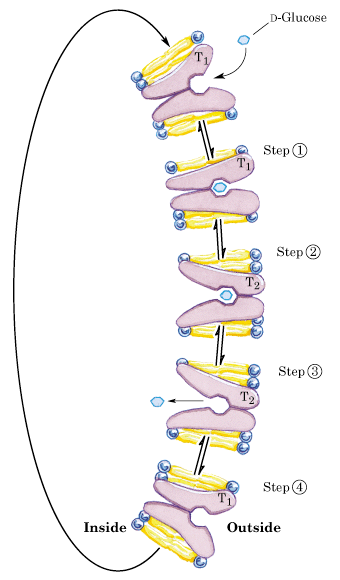
Selectivity can also involve an allosteric conformational change
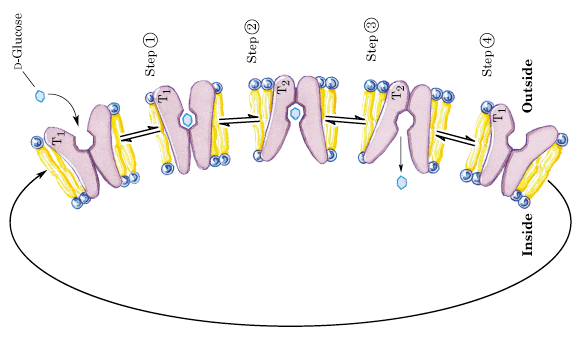
Can this protein move glucose against a concentration gradient?
No. Can only go with a gradient
- Why are transport membrane proteins needed? (permeability and control)
- Transport selectivity (selection based on chemical features)
- Passive versus active transport
- Nerve signal transmission
Channels and carriers move molecules with a concentration gradient
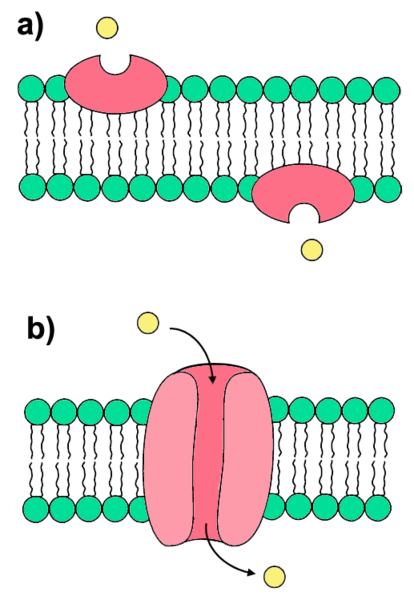
Pumps move molecules against concentration gradients
How does a cell move something against a concentration gradient?
Active transport
Channels and carriers move molecules with a concentration gradient


In active transport, an unfavorable reaction (going against a concentration gradient) is coupled to a favorable reaction ($ATP \rightarrow ADP+P_{i}$).
$\Delta G_{transport} = \Delta G_{conc} + \Delta G_{ATP}$
Coupling between $ATP \rightarrow ADP + P_{i}$ and transport is allosteric conformational change

- Why are transport membrane proteins needed? (permeability and control)
- Transport selectivity (selection based on chemical features)
- Passive versus active transport (active transport requires energy expenditure)
- Nerve signal transmission
How do signals cross meters in our body when even motor proteins would take hours to get that far?
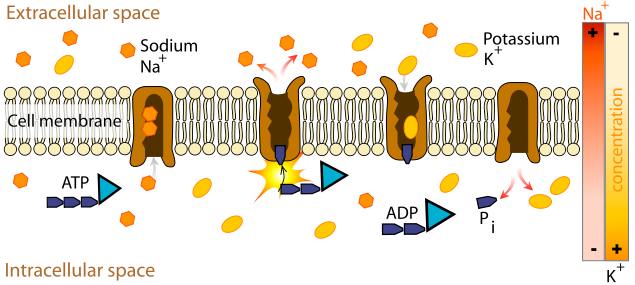
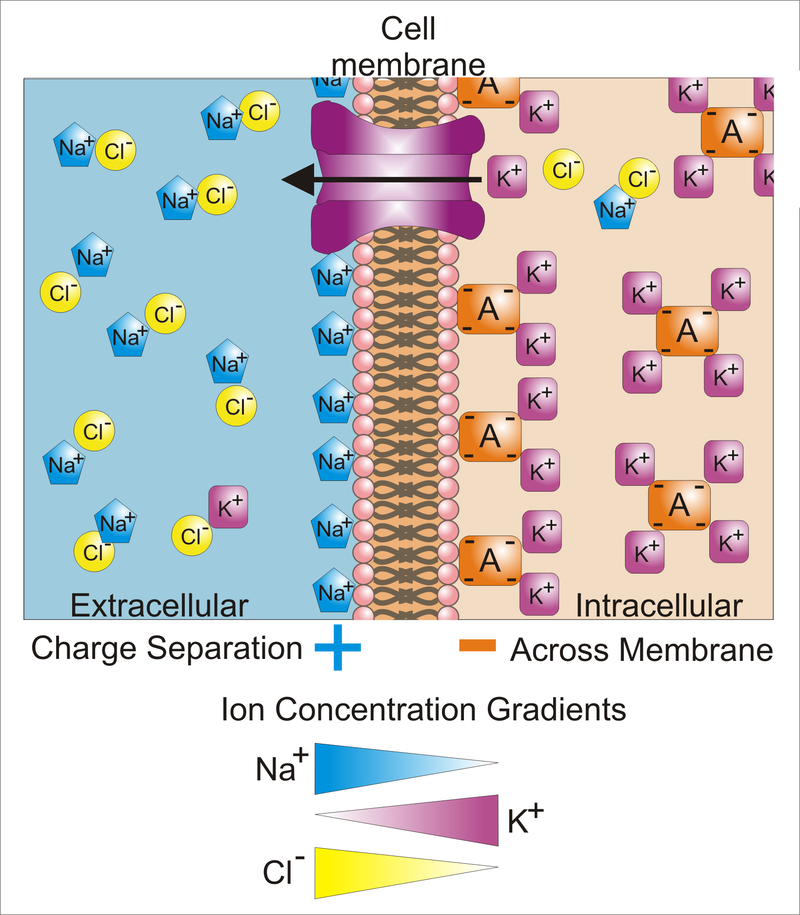
Na+/K+ pumps create electrical potential across the bilayer
Credit: wikimedia.org
What happens if I open a Na+ specific channel (not pump)?

Credit: wikimedia.org
What happens if I open a Na+ specific channel (not pump)?

Na+ ions will rush in, potential difference will drop
Gated ion channels respond to changes in electrical potential (voltage)
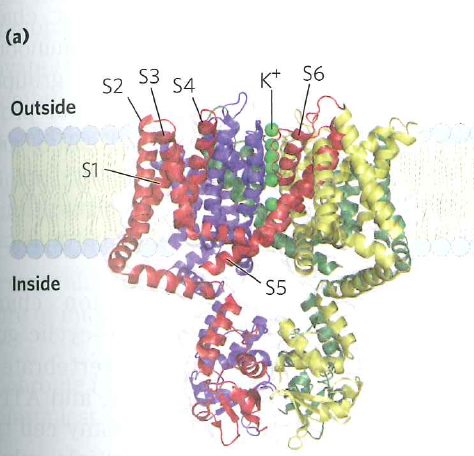
Gated ion channels respond to changes in electrical potential (voltage)
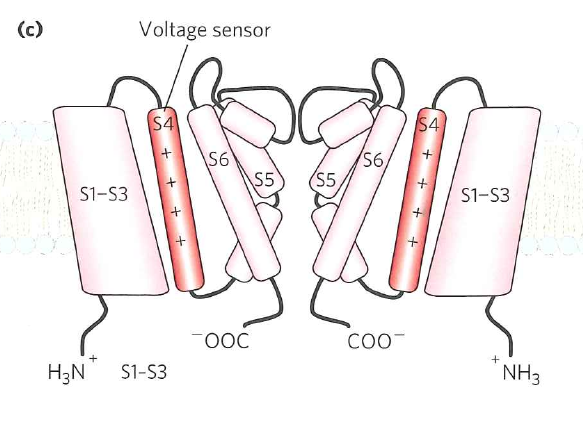
Gated ion channels respond to changes in electrical potential (voltage)
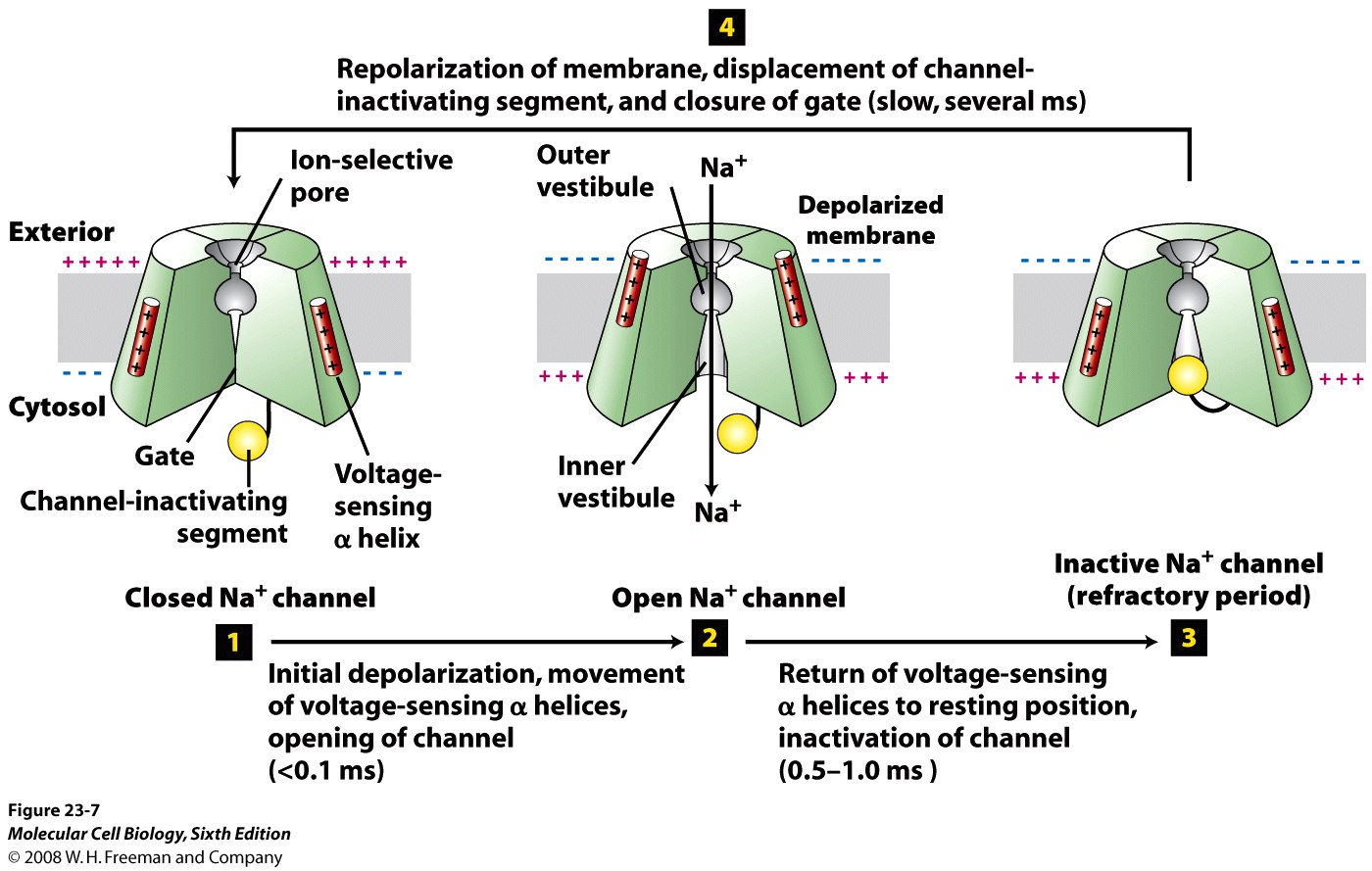
Action potential propagates along the nerve
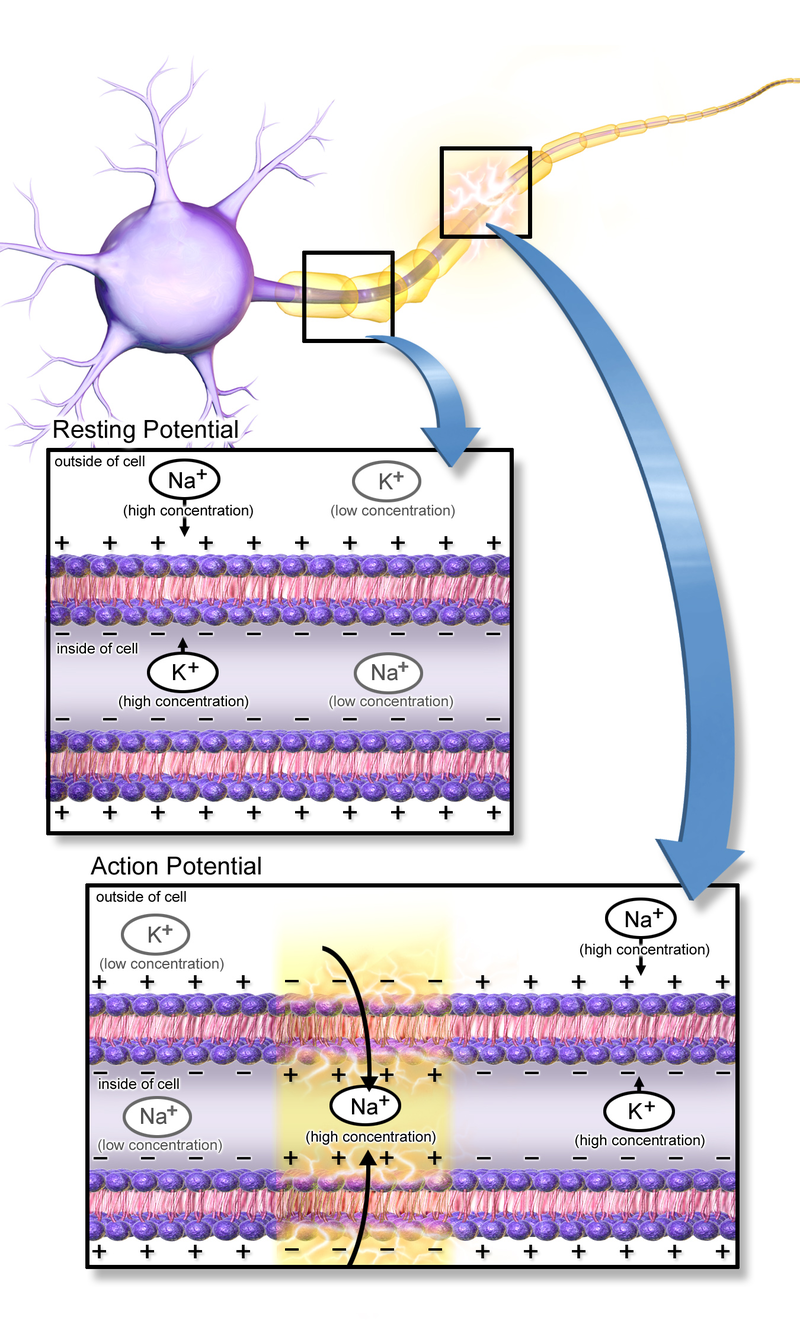
Action potential propagates along the nerve
Resting
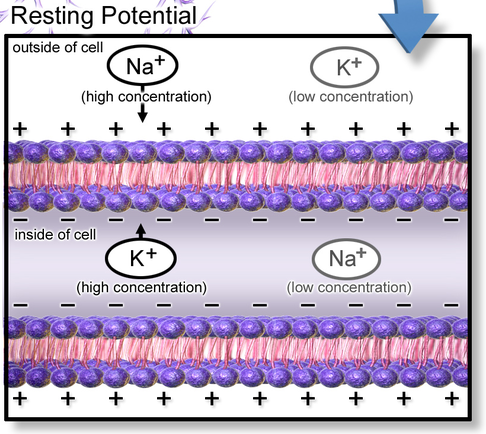
Action potential propagates along the nerve
Propagation
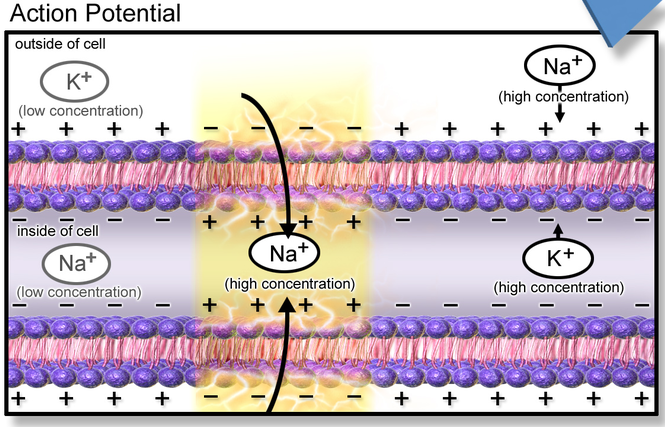
After signal, Na+/K+ pumps restore action potential
- Why are transport membrane proteins needed? (permeability and control)
- Transport selectivity (selection based on chemical features)
- Passive versus active transport (active transport requires energy expenditure)
- Nerve signal transmission (is built on moving ions across membranes in a concerted way)